Nearly six years before an earthquake ravaged Japan’s Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, U.S. regulators came to a sobering realization: seismic risks to nuclear plants in the eastern two-thirds of the country were greater than had been suspected, and engineers might have to rethink reactor designs.
Thus began a little-noticed risk assessment process with far-reaching implications despite its innocuous-sounding name: Generic Issue 199. The process, which was supposed to have been finished nearly a year ago, is still under way. It is unclear when it will be completed.GI-199, as it is known, was triggered by new geophysical data and computer models showing that, as the Nuclear Regulatory Commission put it in an August 2010 summary document, “estimates of the potential for earthquake hazards for some nuclear power plants in the Central and Eastern United States may be larger than previous estimates.”
Data from the U.S. Geological Survey and other sources suggest, for example, that “the rate of earthquake occurrence … is greater than previously recognized” in eastern Tennessee and areas including Charleston, S.C., and New Madrid, Mo., according to the NRC document. There are 11 reactors in Tennessee, South Carolina and Missouri.
GI-199, a collaborative effort between the NRC and the nuclear industry, has taken on new urgency in light of the crisis in Japan. “Updated estimates of seismic hazard values at some of the sites could potentially exceed the design basis” for the plants, the NRC document says.
NRC spokesman Roger Hannah said the exercise was never meant to provide “a definitive estimate of plant-specific seismic risk.” Rather, he said, it was done to see if certain plants “warranted some sort of further scrutiny. It indicates which plants we may want to look at more carefully in terms of actual core damage risk.”
The information collected under GI-199 has been shared with operators of all 104 reactors at 64 sites in the U.S., Hannah said, and NRC officials are in the process of determining whether any plants require retrofits to enhance safety. He added that the assessment indicated “no need for any immediate action. The currently operating plants are all safe from a seismic standpoint.”
Every proposed nuclear plant in the U.S. already must undergo an extensive environmental review that examines the site’s seismology, hydrology and geology, NRC spokesman Joey Ledford said.
The Nuclear Energy Institute, a trade group, said in a statement this week that nuclear plants “are designed to withstand an earthquake equal to the most significant historical event or the maximum projected seismic event and associated tsunami without any breach of safety systems.” The U.S. Geological Survey updates its seismic hazard analyses roughly every six years, the institute said, and “the industry is working with the NRC to develop a methodology for addressing” newly recognized hazards.
Asked why GI-199 has taken nearly six years, Ledford said, “These are very complicated issues. We’re talking about 64 plant sites. It’s not a small task.” According to a January 2010 NRC document, GI-199 was to have been completed last April. An agency document dated January 2011 says the completion date is “to be determined.” The NRC blamed the delay on issues relating to the release of a copyrighted Electric Power Research Institute report to an NRC contractor and on “the desire for internal and external stakeholder agreement.” Over the years, the NRC often has been criticized for taking too long to resolve important safety issues. One example: what’s known in the industry as a loss-of-cooling accident, regarded as the most serious event that can happen at a reactor. Since the 1980s, the NRC has been looking into the problem of clogged emergency core cooling pumps in boiling water reactors. The issue has not been resolved. The Fukushima Daiishi reactor and 35 reactors in the U.S. are boiling water reactors.
Japanese regulators, too, recognized that they had understated seismic risks to their nuclear generating facilities, and were pushing utilities to engineer plants better able to resist tsunamis.
At a previously scheduled NRC conference in suburban Washington last week, just days before the 9.0 earthquake that crippled Fukushima Daiichi, Japanese officials briefed their American counterparts on four quakes in Japan since 2005 that exceeded design standards for some nuclear plants. In no case was the damage severe. Nonetheless, the Japanese were re-evaluating seismic data and moving to buffer the plants.
At the conference, the Japanese delegation said that tsunamis were a particular concern for coastal plants located in seismic zones. The officials said the industry should build upon “significant progress in tsunami hazard assessment, tsunami warning and mitigation and tsunami resistant design.”
EVENTS GET AHEAD OF THE REGULATORS
Earthquakes can occur in all sorts of locales. In January 1986, a late-morning quake measuring 4.96 on the Richter scale was blamed for cracks in the Perry Nuclear Power Plant on Lake Erie near Cleveland. At first, people thought it wasn’t a quake; speculation focused on an explosion somehow related to the Challenger space shuttle disaster or an attack on New York City. The newly licensed plant’s reactor was to be fueled for the first time the next day. Officials and the public were caught by surprise; few suspected Northeastern Ohio was in an active seismic zone. But it is. Experts determined that the quake’s epicenter was 11 miles from the plant, which has been dogged by controversy ever since.
Earthquakes can occur in all sorts of locales. In January 1986, a late-morning quake measuring 4.96 on the Richter scale was blamed for cracks in the Perry Nuclear Power Plant on Lake Erie near Cleveland. At first, people thought it wasn’t a quake; speculation focused on an explosion somehow related to the Challenger space shuttle disaster or an attack on New York City. The newly licensed plant’s reactor was to be fueled for the first time the next day. Officials and the public were caught by surprise; few suspected Northeastern Ohio was in an active seismic zone. But it is. Experts determined that the quake’s epicenter was 11 miles from the plant, which has been dogged by controversy ever since.
A previously unknown fault line also runs near the Indian Point plant, 24 miles north of New York City. Indian Point’s two units are up for relicensing by the NRC in 2013 and 2015, respectively, and a fierce battle is expected. New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo, while campaigning last year, called for Indian Point to be closed. Now he has ordered a safety review of the plant. In a 2008 paper, four researchers from Columbia University reported that “Indian Point is situated at the intersection of the two most striking linear features marking the seismicity and also in the midst of a large population that is at risk in case of an accident at the plants.” Indian Point’s two reactors, the researchers noted, “are located closer to more people at any given distance than any other similar facilities in the United States.”
The plant’s operator, Entergy Corp., issued a statement saying all its nuclear plants “were designed and built to withstand the effects of natural disasters, including earthquakes and catastrophic flooding. The NRC requires that safety-significant structures, systems and components be designed to take into account the most severe natural phenomena historically reported for each site and surrounding area.”
Even where nuclear plants have been built in established zones of potentially severe earthquakes, such as California, scientists are often far ahead of the regulators in raising questions about the safety of the plants. The California Coastal Commission, for example, has been sparring with the NRC over what the commission claims are under-appreciated seismic risks at the San Onofre plant, on the Pacific Ocean south of Los Angeles. After a review several years ago, the commission said “there is credible reason to believe that the design basis earthquake approved by [the NRC] at the time of the licensing of [San Onofre Units] 2 and 3 … may underestimate the seismic risk at the site.” Mark Johnsson, a geologist with the commission, said GI-199 suggests that the NRC is taking such risks more seriously.
“In California, we’ve had our differences with the NRC,” Johnsson said, “but they are saying there is credible evidence the earthquake risk in large portions of the country may have been underestimated for decades. We have objected to things they have done. We have not particularly relied on their work here in California. But in this instance they are trying to get it right, I think. They are looking at the new science and are open to it. Right now, there is insufficient data to understand how these faults work at great depths under these power plants.”
The Coastal Commission has accused the NRC of trying to weaken safety regulations for spent fuel storage sites in areas prone to tsunamis and quakes. It said the most likely incident on the West Coast would involve a major earthquake “immediately followed by inundation of the damaged facility by a tsunami.” That is exactly what happened in Japan.
In a 2002 letter to the NRC, the commission’s executive director, Peter Douglas, said the storage areas should have safety standards “consistent with the requirement for nuclear power plants.” He said the NRC hadn’t offered any logical explanation for trying to weaken the rules.
Douglas wrote, “It is especially important that an appropriate standards for … tsunamis be applied because perhaps the most likely scenario for release of radiation to the environment is damage to an [independent spent fuel storage installation] or [monitored retrievable storage installation] during a major earthquake, immediately followed by inundation of the damaged facility by a tsunami.”
The NRC rejected Douglas’s complaint and lowered the seismic standards for spent fuel storage.
Joe Litehiser, a Bechtel Corp. researcher, has studied the implications of earthquakes on licensing of proposed new nuclear plants in the central and eastern U.S. Litehiser said there is more seismological information available now than there was decades ago, when the existing plants were built. Scientists now believe, for example, that major earthquakes occur around Charleston, S.C., every 550 years instead of several thousand years apart, as industry models had assumed.
This is relevant not only because South Carolina has seven active reactors, but because four more units are planned for the state. Applications filed by the proposed operators, Duke Energy and South Carolina Electric & Gas, seek NRC permission to build Westinghouse Advanced Passive 1000 (AP1000) reactors in Fairfield and Cherokee counties. In a March 7 letter to NRC Chairman Gregory Jaczko, U.S. Rep. Edward Markey, D-Mass., wrote that one of the agency’s own experts believes the AP1000’s shield building could “shatter like a glass cup” in the event of an earthquake or a similar disaster.
Aaron Mehta and Susan Stranahan contributed to this story.
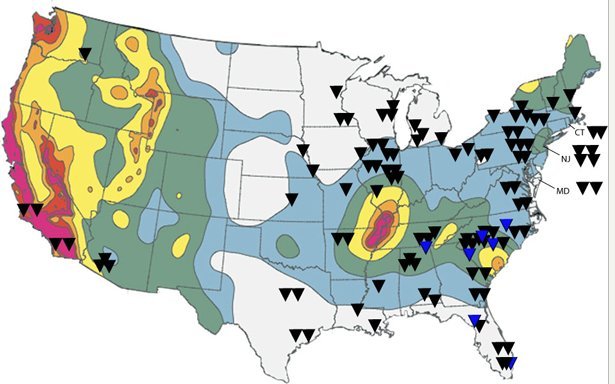
What are the risks of an earthquake beneath a reactor near you? This image combines a 2006map by the United States Geological Survey showing varying seismic hazards across the U.S. with locations of nuclear reactors. Reactors in black are active; reactors in blue are proposed sites for the new model known as the AP1000. Probability of strong shaking increases from very low (white), to moderate (blue, green, and yellow), to high (orange, pink, and red). Credit: Kimberly Leonard/Center for Public Integrity.
For more information on each nuclear reactor in our map, download the list." target="_hplink"> map by the United States Geological Survey showing varying seismic hazards across the U.S. with locations of nuclear reactors. Reactors in black are active; reactors in blue are proposed sites for the new model known as the AP1000. Probability of strong shaking increases from very low (white), to moderate (blue, green, and yellow), to high (orange, pink, and red). Credit: Kimberly Leonard/Center for Public Integrity.
No comments:
Post a Comment